Separating Oil from Water, Decreasing the Amount of Oil in the World's Oceans
Grade 5
Presentation
No video provided
Hypothesis
Hypothesis:
Manipulate: type of oil removal strategy
Responding (measuring) oil left in the container after the procedure
If the oil removal type is changed then I will see a different amount of oil in each container and the one with the least amount of oil in it after is the winner or the best.
|
1 (best) |
Oil only sorbent pad |
|
2 |
Absorb-all |
|
3 (medium) |
Micro Blaze |
|
4 |
Sawdust |
|
5 (worst) |
Oil skimmer |
Research
|
Bauer’s Research Summary: Some things mix easily in water, other things do not. This is because water molecules are “polar molecules.” This means that one end of the water molecule is positively charged and one end is negatively charged. Oil molecules are negative so they will not mix with water. Also water molecules are very dense, and oil molecules are not. Water molecules do not want to break their bonds which makes it impossible for the oil to dissolve in it. Tools that have been effective so far in cleaning up oil spills include the Oil Boom. A boom is a floating barrier that can be made of plastic or metal that keeps oil contained. The Oil Skimmer is meant to skim the oil on the top of the ocean. Sorbents can be sawdust, hay, peat moss, straw and ground up corn cobs. Absorb-all is also a sorbent. Situ Burning is a technique where crews light the oil on the surface of the ocean on fire so the oil is burned off. Dispersants are chemicals that break down oil much like dish soap. How they work is they break the oil into much smaller droplets breaking up the oil slick and letting the ocean absorb the oil. High pressure hot water washing cleans the shoreline by washing the oil off the rocks. The oil is trapped by oil booms so it can be skimmed or removed by another method. Oil absorbent pads have many layers so they can trap the oil inside. The oil only ones do not absorb water so you can put them on top of oil and water and they just suck up the oil. Oil spilled in water can affect the plants and animals living in that water in many ways. First the oil is poisonous to many living things. The organisms inhale or ingest the toxic oil poisoning them or they absorb it through their skin. The oil can also cover them, smothering small animals or coating feathers and fur causing them to not be able to maintain their body temperature. The oil also makes fish and shellfish unsuitable for humans to eat. The clean up operations can also affect plants and animals. OIl spills can affect animals in 3 main ways. By ingesting it or the oil coming in contact with their food. If the animal ends up eating the oil, it can cause poor health like ulcers, internal bleeding or diarrhea. If the animal absorbs the oil into their skin, it can cause liver or kidney damage and also cause reproductive failure. Inhaling or breathing in the oil on the surface can cause the animal to have irritation to the lungs or breathing problems. Indirect issues can also come from oil spills. It may cause all the animals to relocate to a new home and it may cause changes to the animals natural life cycle. An emulsifier means that when you mix something, it can mix so well that it completely blends together. A good example would be at home when you are making homemade salad dressing and the oil and vinegar mixes very well together. |
Variables
Controlled Variables:
Water temperature
Water volume
Size and shape of container
Amount of oil added
Test time for each sample
Amount of oil absorber added
Strainer size for stained samples
Manipulated variables:
Micro-blaze
Oil only sorbent pad
Sawdust
Absorb-all
Oil skimmer
Extraction techniques
Procedure
Experimental Procedure:
- Tupperware containers (5)
- Fill each container half full with water
- Add ¼ cup motor oil to each container
- For container 1: Oil only sorbent: set the oil only sorbent pads on top of the liquid for (time?)
- For container 2: Boom and skimmer: use a teaspoon to move the oil to one side of the container and then scoop it out.
- For container 3: Sawdust sorbent: Sprinkle ¼ cup of fine sawdust over the liquid, then <poor the mixture through a sieve
- For container 4: Absorb-al ¼ cup of Absorb-al in the container then poor though a sieve
- For container 5: Micro Blaze add ¼ cup of Micro Blaze to container
- Measure the remaining oil in each container using a 1 cm square grid on transparency paper.
- Repeat each test 3 times
Observations
The oil skimmer worked very well
The the water under the absorb-all was very grey
The oil only sorbent pad worked well but needed another one to absorb all the oil
The sawdust was very chunky
The sawdust water was very transparent
The oil only sorbent pad was very transparent
The evaluation grid had residue on it that looked like dried salt after the experiment
The oil floated on top of the water very well
When we poured the oil in there was lots of little droplets of it, but over time it all came back together on the surface
The oil skimmer scooped mostly oil and little water
The Micro-Blaze emulsified a lot
The sawdust and absorb-all emulsified during straining
Analysis
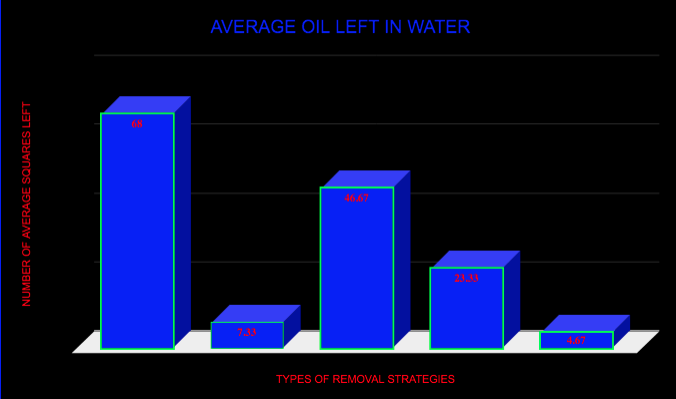
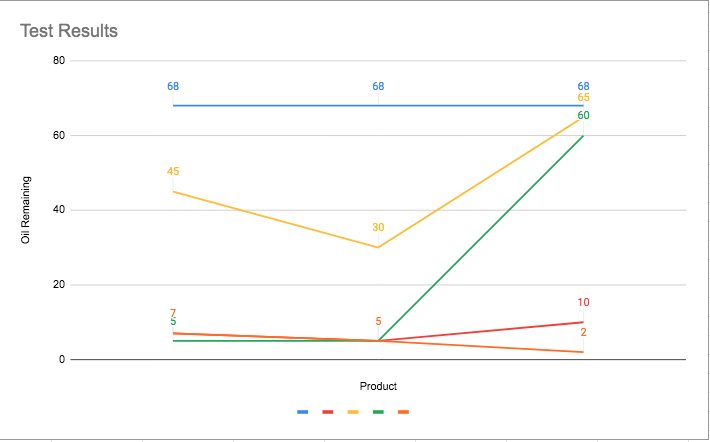
The results of my project were not as I expected. In the begining I beleived that the Oil only sorbent pad would do the best at removong oil in this experiment. However the most simple of my oil removal stratagies turmed out to be the most effective. The oil skimming spoon worked the best out of everything.
Conclusion
Conclusion
The results from this experiment surprised me and were different from my hypothesis. This experiment was harder than I thought it would be because the evaluation grid did not work well. I expected all of the remaining oil in the samples to float on the top of the water. This did not happen and the evaluation grid was not super accurate. Some of the test samples had oil mixed throughout the sample because of the way we separated the sorbent, the water and the oil.
Micro Blaze has microbes that eat the oil. I think that my experiment did not have enough time to work. It takes 15-20 min to start working and my test procedure samples only sat for 10 mins. I think the micro blaze emulsified the oil and water.
Oil only sorbent pad performed really well. There was not enough absorbent capacity to capture all of the oil. It did a very good job of keeping the oil on the surface of the water which made the evaluation grid a lot easier. I think this is a great oil removal strategy and if I were to add another oil pad it would have absorbed all of the oil.
Absorb-all did not perform how I thought it would. I think that part of the problem was the extraction method we used. We added the absorb-all, then let it sit for 10 mins. When we poured it through a strainer it mixed a lot, so like the micro blaze it emulsified a lot, which made the evaluation grid really hard. I think this oil collection product would work better for oil spilled on harder surfaces than for oil in water.
Saw dust worked better than I expected. Much like absorb-all, our extraction method did not work the best because of the mixing that occurred when I poured it through the strainer. Similar to absorb-all, I believe that it is better suited for hard surfaces where it can absorb the oil then be swept up and disposed of. Saw dust is a neat option because it is natural, safe and it can be fun to make.
Oil skimmer. My hypothesis was completely wrong and it did way better than expected. I was surprised how little water I got in every spoon of water. Although this method was really effective I would not want to clean up a big ocean oil spill with just a spoon. The little bubbles left on the surface made it tough to use the evaluation grid. With this method the oil remained on the surface of the water and did not cause it to mix with the water below like some of the other methods. I know this because of how transparent the water stayed.
All the methods I tested worked to remove oil from water however they all worked differently. Some worked better than others but it was difficult to determine how much oil each method removed. Based on my results, if l had to clean up an oil spill in water I would choose an oil skimmer and oil absorbent pad.
Application
The results from this project could be used in the ocean or other fresh water areas such as lakes and streams. The methods that were tested could easily be used for real oil spills and clean up in the environment. The products I used were easily found and I beleive that they could be very useful to help out in the real world.
Sources Of Error
My main source of error was the evaluation grid that I used. I do not beleive it was completly accurate. If I could change how I evaluated the amount of oil left in the jars, I would not use the grid again. I would find an alternative to measure it.
I also had an error of using fresh water with the oil. Since I am considering this to help clean up the oceans, I should have tried to use salt water mixed with the oil. However I do beleive that there is an application for my project in fresh water as well. There is also oil spills that have occured in lakes and streams as well.
Also this project was done in my home and not a huge science lab. It could not be 100% accurate because of this.
Citations
Title:Why Don't Oil and Water Mix?
Website title:Wonderopolis
URL:https://wonderopolis.org/wonder/why-dont-oil-and-water-mix
Published year:Missing
Date accessed:March 9, 2024
Contributors:Missing
Title:Why Don't Oil and Water Mix? - Chemistry for Kids | Mocomi
Website title:Mocomi Kids
URL:https://mocomi.com/why-oil-and-water-dont-mix/
Published year:Missing
Date accessed:March 9, 2024
Contributors:Missing
Title:Missing
Website title:Why oil and water do not mix
URL:https://web.fscj.edu/Milczanowski/psc/lect/Ch10/slide10.htm
Published year:Missing
Date accessed:March 9, 2024
Contributors:Missing
Title:10 Methods for Oil Spill Cleanup at Sea
Website title:Marine Insight
URL:https://www.marineinsight.com/environment/10-methods-for-oil-spill-cleanup-at-sea/
Date published:March 28, 2022
Date accessed:March 9, 2024
Author:Mayur Agarwal
Title:How to clean up oil spills - 14 unique methods
Website title:Nautilus Shipping
URL:https://www.nautilusshipping.com/oil-spill-clean-up-methods
Date published:October 20, 2022
Date accessed:March 9, 2024
Contributors:Missing
Title:How does NOAA help clean up oil and chemical spills?
Website title:NOAA's National Ocean Service
URL:https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/spills-cleanup.html
Date published:January 18, 2024
Date accessed:March 9, 2024
Contributors:Missing
Title:How Oil Harms Animals and Plants in Marine Environments
Website title:NOAA's Office of Response and Restoration
Published year:Missing
Date accessed:March 9, 2024
Contributors:Missing
Title:How does oil impact marine life?
Website title:NOAA's National Ocean Service
URL:https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/oilimpacts.html
Date published:August 24, 2023
Date accessed:March 9, 2024
Contributors:Missing
Title:Missing
Website title:WEC285/UW330: Effects of Oil Spills on Marine and Coastal Wildlife
URL:https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/UW330
Published year:Missing
Date accessed:March 9, 2024
Contributors:Missing
Title:Emulsify - Definition, Meaning & Synonyms
Website title:Vocabulary.com
URL:https://www.vocabulary.com/dictionary/emulsify
Published year:Missing
Date accessed:March 9, 2024
Contributors:Missing
Acknowledgement
I had help from:
Ms. Webber
Ms. Summerscales
Mom
Dad

