Desalinating our Oceans
Grade 5
Presentation
No video provided
Hypothesis
If the light source and tempature of the water are altered, then the quantity of salt remaining in the water will be impacted.
We think that the Hot,Hot design would work the best.
Research
|
How can we make a desalinator? Date: Nov. 30 2023 |
To make your desalinators, you will need:
|
|
How can we measure the amount of salt left in the water? Date: Jan.11 2024 |
Get a multimeter to make different tests. The red cord is positive and the black cord is negative. There are other options but the multimeter is a better choice. |
|
How do we use a multimeter? Date: Jan. 25 2024 |
Multimeters are testing how much salinity is left in the saltwater. |
|
What are we going to use to measure the salinity in the water? Date: Jan 30 2024 |
Hydrometer Salinometer Handheld refractometer$20 Salinity meter-$30-40 Salinity meter tests temperature and it measures the salt in the saltwater. |
|
What does ppm stand for? Date: Mar. 2 2024 |
Salinity measurement: parts per million. |
|
How much is the salt in 1 cup of ocean water? Date: Mar. 5 2024 |
2.5 level teaspoons |
|
How do the different stages of the water cycle happen? Date: Mar. 5 2024 Evaporation |
Evaporation:The warmer the air, the more water vapor the air can hold. Evaporation happens when the molecules in the water heat up then they release and float around in the air. |
|
Condensation Date: Mar. 5 2024 |
Condensation: Either the air is cooled to its dew point or it becomes so saturated with water vapor that it cannot hold any more water and then falls. |
|
Precipitation Date: Mar. 5 2024 |
Precipitation: When so much water has condensed that the air cannot hold it anymore. The clouds get heavy and water falls back to the earth in the form of rain, hail, sleet or snow. |
Variables
MANIPULATED VARIABLES: Temperature of the water, Light source the desalinator is exposed to.
CONTROL VARIABLES: Materials, Procedure, Amount of time they are left for.
RESPONDING VARIABLES: Amount of salt left in the water.
Procedure
- In a large bowl add 4 cups of water and 10 teaspoons of salt. Stir until dissolved.
- Pans with hot water label: Hot W,Hot L and Hot W,Cold L. Pans with cold water label: Cold W,Hot L and Cold W,Cold L. (The L and W stand for light and water)
- Scoop 1 cup of the salt water into each of 2 pans. Heat the remaining two cups of water and put in the other 2 pans.
- Use the salinity meter to test the amount of salt and temperature in the water. Make sure they all have an equal amount of salt. Record the numbers.
- Place the small container in the center of the foil pan with the water.
- Place a small rock into each container so that it doesn't float.
- Cover the pan in plastic wrap and pull tight. Use tape to keep the plastic wrap tight if needed.
- Put 2 coins on the plastic wrap right above the small cup so it is just slightly lower than the rest.
- Pans labeled ___,Hot place under the Heat lamp. Pans labeled ___,Cold place under the LED light.
- Place each desalinator 4.5 inches away from the light.
- Let the desalinators sit for 24 hours.
- After 24h use the salinity meter to test the amount of salt left in the water that is in the small container and record. If you want you can measure the salinity of the water in the foil pan as well to see if it is higher. Make sure to measure the amount of salinity in normal tap water as well so you know the starting point. You can also search up how clean the water has to be to safely drink it in your country.
Observations
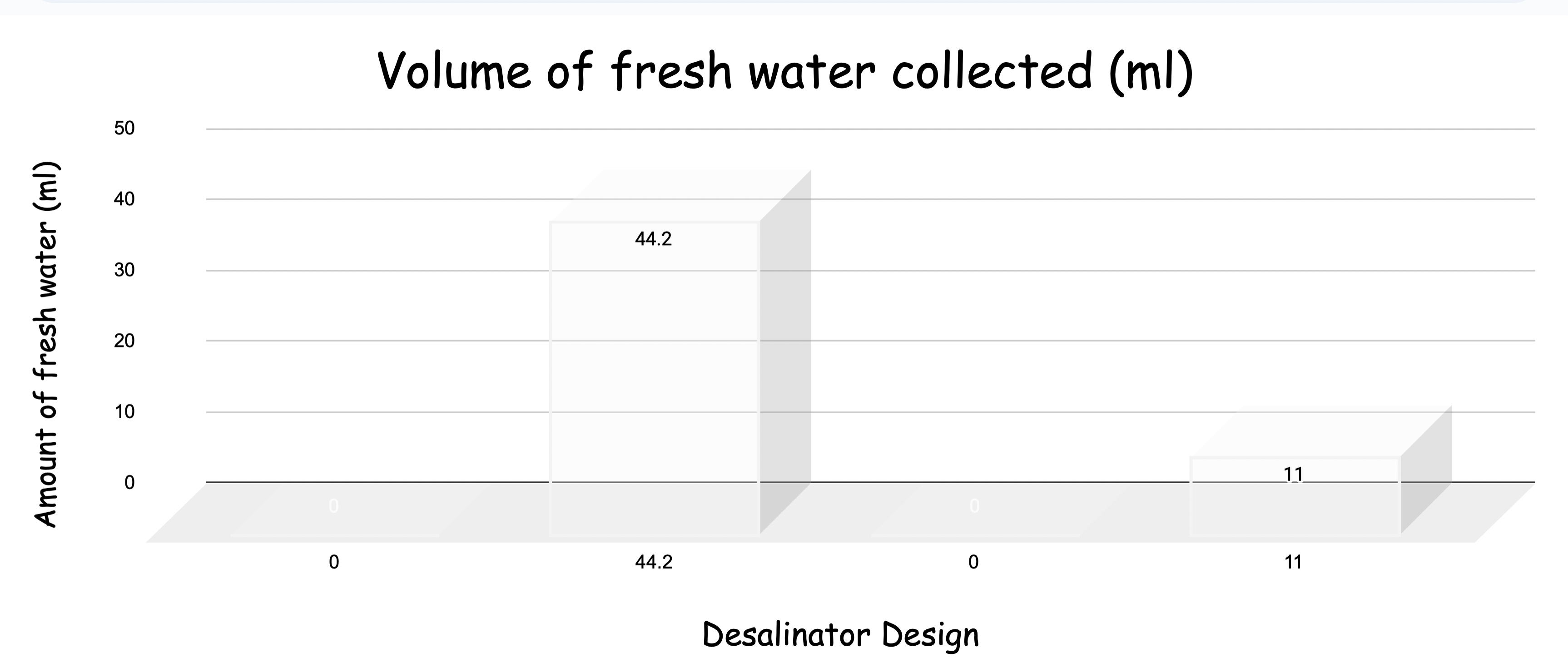
- The desalinators under the LED light didn't produce any freshwater
- The desalinators with the hot water steamed up right away and then didn't do very much in the next 24 hours.
- All the wrinkles in the plastic wrap trapped the condensed water and made it drip back into the outer pand instead of the inner cup.
Analysis
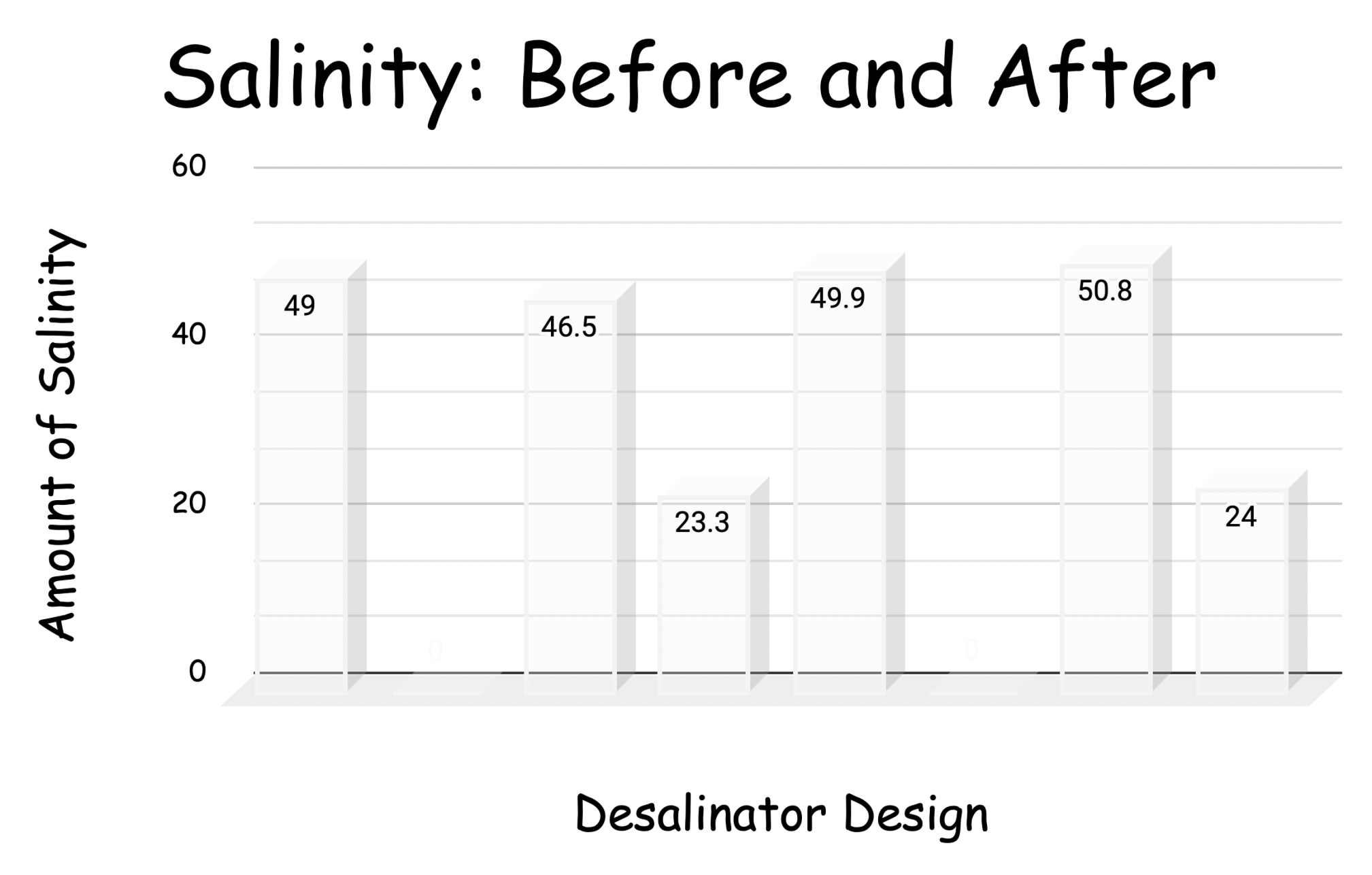
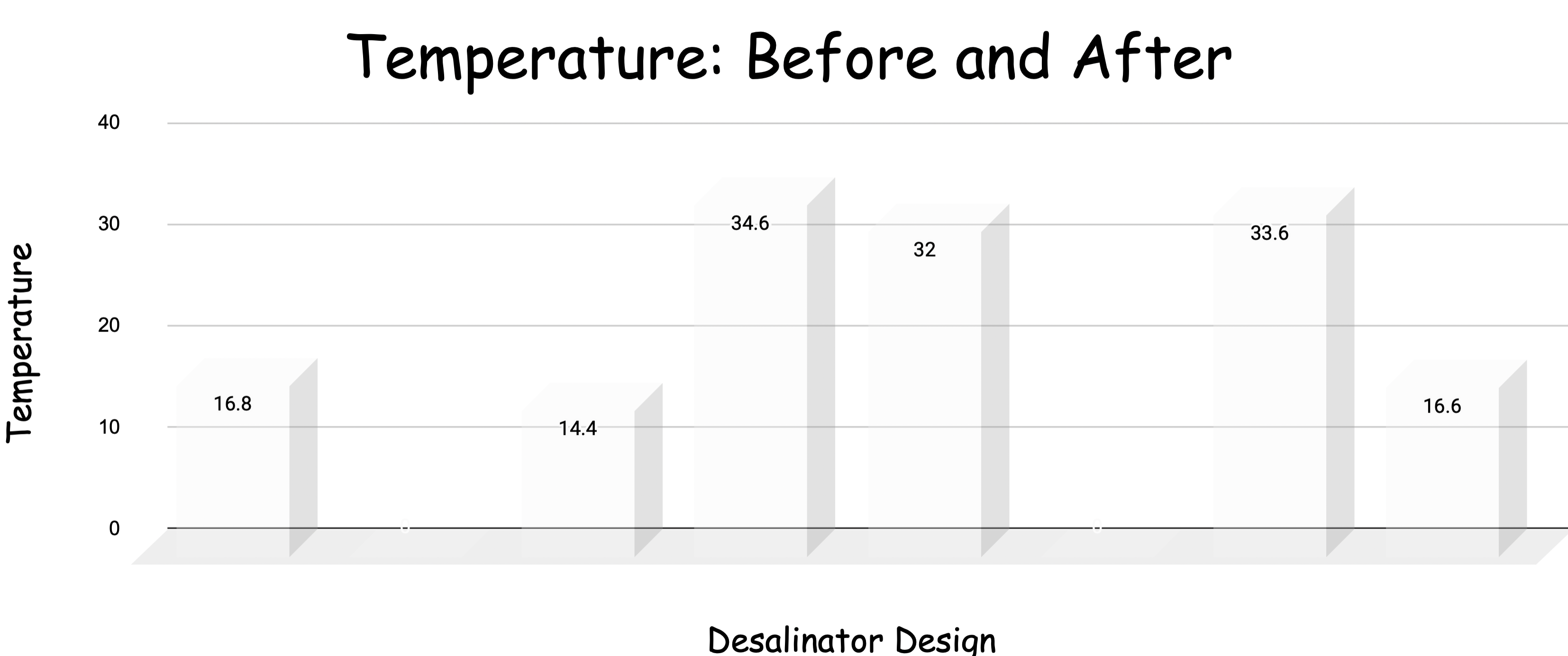
Our conclusion was that the cold water hot light worked best/produced the most fresh water. It was unexpected that the desalinator with the cold water and hot light produced the most fresh water. We think that this happened because the tempature changing so fast had
something to do with helping the water evaporate and condense.
Conclusion
In this experiment we studied different ways to desalinate water. We tested different designs of desalinators, by measuring the salinity and amount of clean water the different designs produced.
We found that the Cold water,Hot light design produced the most amount of freshwater.
Our hypothesis was incorrect. We thought that the Hot W,Hot L would produce the most fresh water although after the experiment we found the Cold W,Hot L produced the most fresh water.
Some unexpected results were that the Hot W, Hot L didn’t produce the most fresh water. We do not know why this unexpected result happened, although we are wondering if maybe the temperature difference caused more condensation.
The desalinators with the cold light (LED) did not produce any condensation or water for us to measure the temperature or the salinity.
Changing the light source the desalinator is exposed to majorly changes the amount of water the desalinator is able to produce. Changing the temperature of the water appears to affect the amount of water the desalinator is able to produce.
Application
If people are running out of fresh water but they live by an ocean then they can desalinate it and then have fresh water to drink or cook safely although they would have to filter it to remove any other bacteria or germs in the water.
Sources Of Error
- Not enough surface area for the water to evaporate.
- The light was too hot it melted the plastic wrap.
- The tape x prevented the condensed water from dripping into the cup.
- The salinity meter was not very acurate.
- We had trouble getting stuff to stay on the trifold.
Citations
Acknowledgement
1. Ms. Webber
2. Ms .Summerscales
3. Ms. Fortmuller
4. Mom (2)
5. Dad (2)
6. Banded Peak

